The Amazon area

The
Amazon area
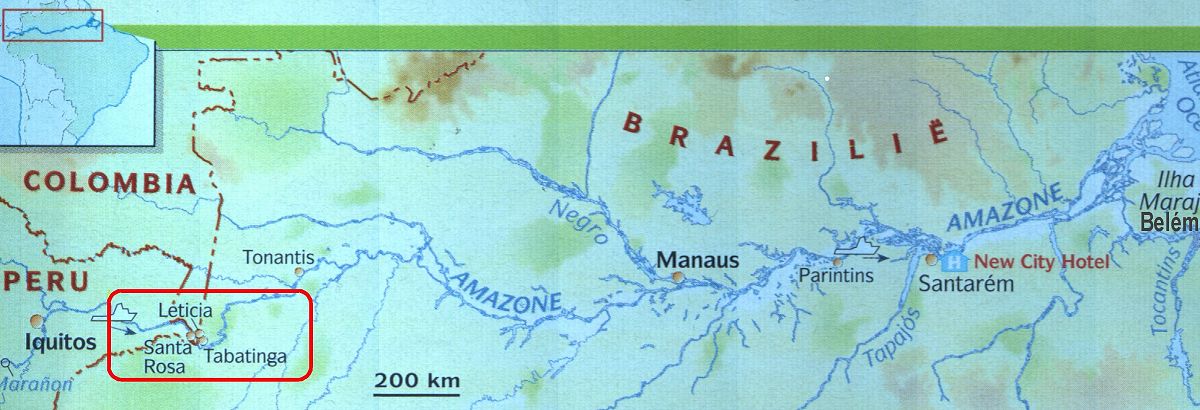
The source of the Amazon starts high in the Peruvian Andes in the west of the South American continent. On his way the Amazon passes places like Iquitos in Peru and Leticia in Colombia. After these places it flows straight through Brazil to the "finish" in the Atlantic Ocean near the place Belem. During it's journey the Amazon receives -directly or indirectly- water from over 15.000 tributaries, 12 of which are over 1500 km in length. The longest, the Madeira -Mamore- Grande at a length of 3200 km is the worlds longest tributary and 14th longest river. In the flood season some two million kilometers of waterways are navigable.
At
the border of the 3 countries Colombia, Peru and Brazil (tres fronteras / three
frontiers) is, in Colombia, the town Leticia. Here are 2 important tributaries
which are namely:
- The "Putumayo". This river is the border between Peru and Colombia
(in the North).
- The "Javari".
This river is the border between Peru and Brazil (in the South).
|
During flood season, the little islands you can find in the river, often disappear under water. Every time the high water remove parts of these islands and leave them at another place. Some will be destroyed, others recreated, but all will be transformed. As the floods decline the silt which is leaved behind, makes the soil very fertile. This fertilized soil is, for instance, used for the grown of big watermelons. |